Mount Elizabeth Novena Hospital #10-48/49

Parkway East Hospital #05-08

Farrer Park Medical Centre #14-12

Mount Alvernia Hospital #08-62

Gleanagles Hospital #06-16
WHAT IS COLONOSCOPY?
A
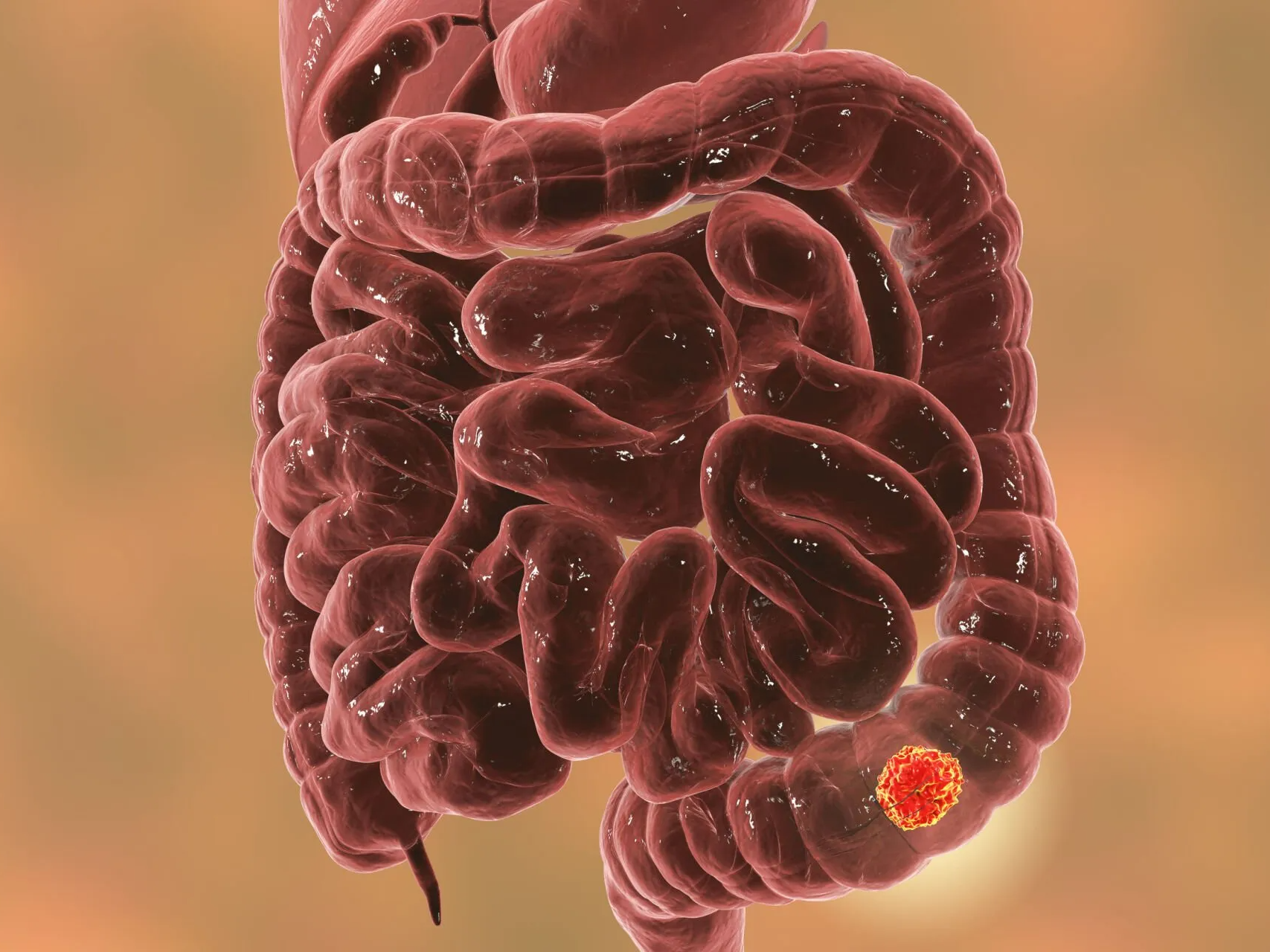
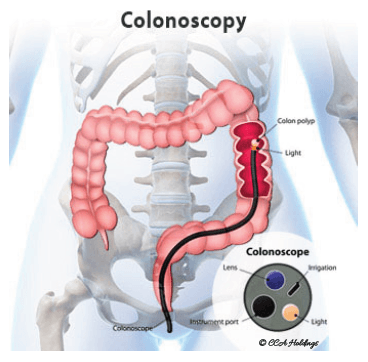
colonoscopy is a test that enables your surgeon to look at the inner lining of your large intestine (rectum and colon). A flexible fibre optic endoscope called a colonoscope, is inserted through the anus to look for ulcers, polyps, tumors or areas of inflammation or bleeding.
WHO SHOULD HAVE A COLONOSCOPY?
Colonoscopy is recommended for all adults aged 50 years or older as part of a colorectal cancer screening programme. Patients with a family history of colon or rectal cancer or polyps are advised to have their colonoscopy performed at an earlier age.
WHAT IS COLONOSCOPY SCREENING?
Colonoscopy screening uses colonoscopy as a preventive measure to detect colorectal cancer or pre-cancerous growths known as polyps early when they are highly treatable. This screening method can prevent colorectal cancer from progressing and improve the probability of successful treatment if cancer is discovered.
WHAT IS COLORECTAL CANCER SCREENING?
Colorectal cancer screening refers to a range of tests and procedures aimed at identifying abnormalities in the colon or rectum that may indicate the presence of colorectal cancer or pre-cancerous conditions. These screening methods are designed to detect cancer early, often before symptoms develop when it is most treatable. Common colorectal cancer screening tests include:
Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT): This test detects blood in the stool, one of the signs of colorectal cancer or polyps. It involves collecting stool samples and sending them to a laboratory for analysis.
Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT): Similar to FOBT, FIT detects blood in the stool but is more specific to human blood and does not require dietary restrictions.
Stool DNA Test (sDNA): This test looks for specific DNA changes in stool samples associated with colorectal cancer or polyps.
Flexible Sigmoidoscopy: A procedure that involves examining the lower section of the colon and rectum using a flexible tube with a camera attached (sigmoidoscope).
Virtual Colonoscopy (CT Colonography): A non-invasive imaging test that uses computed tomography (CT) scans to create detailed images of the colon and rectum.
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF COLONOSCOPY SCREENING?
Early detection of colorectal cancer: A colonoscopy can detect colorectal cancer at an early stage, often before symptoms develop.
Detection and removal of precancerous polyps: If pre-cancerous polyps are discovered, they can be nipped immediately, preventing colorectal cancer from developing.
Comprehensive colon examination: Colonoscopy provides a complete view of the entire colon and rectum, allowing thorough evaluation and reducing the likelihood of missed abnormalities.
High accuracy: Colonoscopy is highly accurate in detecting abnormalities in the colon, including polyps, tumours, inflammation, and other gastrointestinal conditions.
Personalised screening recommendations: Healthcare providers can provide personalised recommendations for future screening intervals and preventive measures based on the colonoscopy findings and individual risk factors.
Peace of mind: Undergoing a colonoscopy provides peace of mind, knowing that you have taken proactive steps to protect your colon health.
WHY UNDERGO A COLONOSCOPY?
- Evaluate the cause of blood in stools or rectal bleeding
- Evaluate the cause of any recent changes in bowel habits
- Evaluate the cause of dark or black stools
- Check for the cause of iron deficiency anemia
- Evaluate the cause of sudden, unexplained weight loss
- Evaluate the colon after abnormal results from a CT scan, MRI, virtual colonoscopy, stool test, or barium enema
- Monitor the efficacy of treatment of inflammatory bowel conditions
- Evaluate abdominal pain
HOW OFTEN SHOULD YOU GET A COLONOSCOPY?
The frequency of colonoscopy screenings depends on individual risk factors and medical history. For most individuals at average risk, a colonoscopy is recommended every ten years, starting at the age of 45. However, individuals with a family history of colorectal cancer or other risk factors may need more frequent screenings, as advised by their healthcare provider.
HOW IS A COLONOSCOPY PERFORMED?
Before the test, you will need to clean out your colon. One to two days before a colonoscopy, our surgeons will instruct you to:
- Adopt a restricted diet low in fibre
- Consume prescription laxative solution that will result in mechanical cleansing of the entire colon
- Drink plenty of clear fluids to prevent dehydration
* You will receive a detailed instruction sheet on these points prior to your procedure
During the test, an intravenous (IV) sedative will be administered to you to help you to relax and fall into light sleep during the test. Air is used to gently inflate the colon as the colonoscope is introduced.
This facilitates the thorough evaluation of the colonic wall. Instruments can be introduced through the colonoscope to allow the surgeon to take biopsies, remove polyps, mark the sites and apply clips.
*You may feel the need to have a bowel movement while the scope is in your colon. You may also feel some cramping. Breathe deeply and slowly through your mouth to relax. This should help the cramping”.
After the test, you can expect to stay at the endoscopy centre for 1 to 2 hours prior to being discharged.
If you have received a sedative, do not drive, operate machinery, or sign legal documents for 24 hours after the test. Arrange to have someone drive you home.
WHAT IS THE COST OF A COLONOSCOPY IN SINGAPORE?
In Singapore, the cost of a colonoscopy will depend on the healthcare provider, facility fees, anaesthesia costs, and additional services required. Generally, it ranges from several hundred to a few thousand dollars. You should check with your healthcare provider and insurance coverage for specific cost details.
WHAT ARE THE RISKS OF COLONOSCOPY?
A colonoscopy is a safe procedure, but there are some risks involved, including:
- Bleeding: In rare cases, removing polyps or tissue samples during colonoscopy may cause bleeding.
- Perforation: There is a slight risk of puncturing the colon wall during the procedure, which may require surgical intervention to repair.
- Adverse Reaction to Anesthesia: Some individuals may experience adverse reactions to the sedative medication used during colonoscopy.
WHAT TO LOOK OUT FOR AFTER COLONOSCOPY?
Adverse reaction to the sedative used during the examination. Bleeding from the site where a tissue sample (biopsy) was taken or a polyp was removed.
CALL YOUR DOCTOR IMMEDIATELY IF YOU EXPERIENCE THESE SYMPTOMS:
After a colonoscopy, it's normal to experience mild side effects such as bloating, gas, or a mild sore throat from the anaesthesia. However, contact your doctor immediately if you experience if you:
- Notice rectal bleeding
- Have severe abdominal pain
- Develop a fever
- Feel very dizzy
- Experience vomiting
- Experience abdominal distention
ABOUT COLORECTAL CLINIC ASSOCIATES
Colorectal Clinic Associates (CCA) is committed towards delivering quality healthcare and medical excellence built on the values of respect, compassion and integrity regardless of race, language and religion.
PRIVACY POLICY
CONTACT
OPERATING HOURS
Monday – Friday: 9am - 6pm
Saturdays: 9am - 1pm
Sunday & Public Holidays:
By appointments
CLINIC LOCATIONS
Mount Elizabeth Novena Hospital
38 Irrawaddy Road
#10-48/49
Singapore 329563
Fax: +65 6643 9929
Parkway East Hospital
#05-08, 319 Joo Chiat Place
Singapore 427989
Fax: +65 6348 1383
Mount Alvernia Hospital
#08-62, Medical Centre D
820 Thomson Road
Singapore 574623
Fax: +65 6250 0537
Gleneagles Hospital
6 Napier Road #06-16
Singapore 258499
Fax:
+65 6993 8624
Connexion
Farrer Park Medical Centre #14-12
1 Farrer Park Station Road
Singapore 217562
Fax: +65 6538 2790
Colorectal Clinic Associates. All Rights Reserved.
Website Designed by Heroes Of Digital.