Mount Elizabeth Novena Hospital #10-48/49
WHAT IS HERNIA SURGERY?
Hernias pose a significant challenge as they tend to cause discomfort and pain. When conventional treatments prove ineffective in alleviating the symptoms of this protruding bulge, the question arises: how can one effectively address hernia? Read on to find out.
WHAT IS A HERNIA, AND HOW DOES IT DEVELOP?
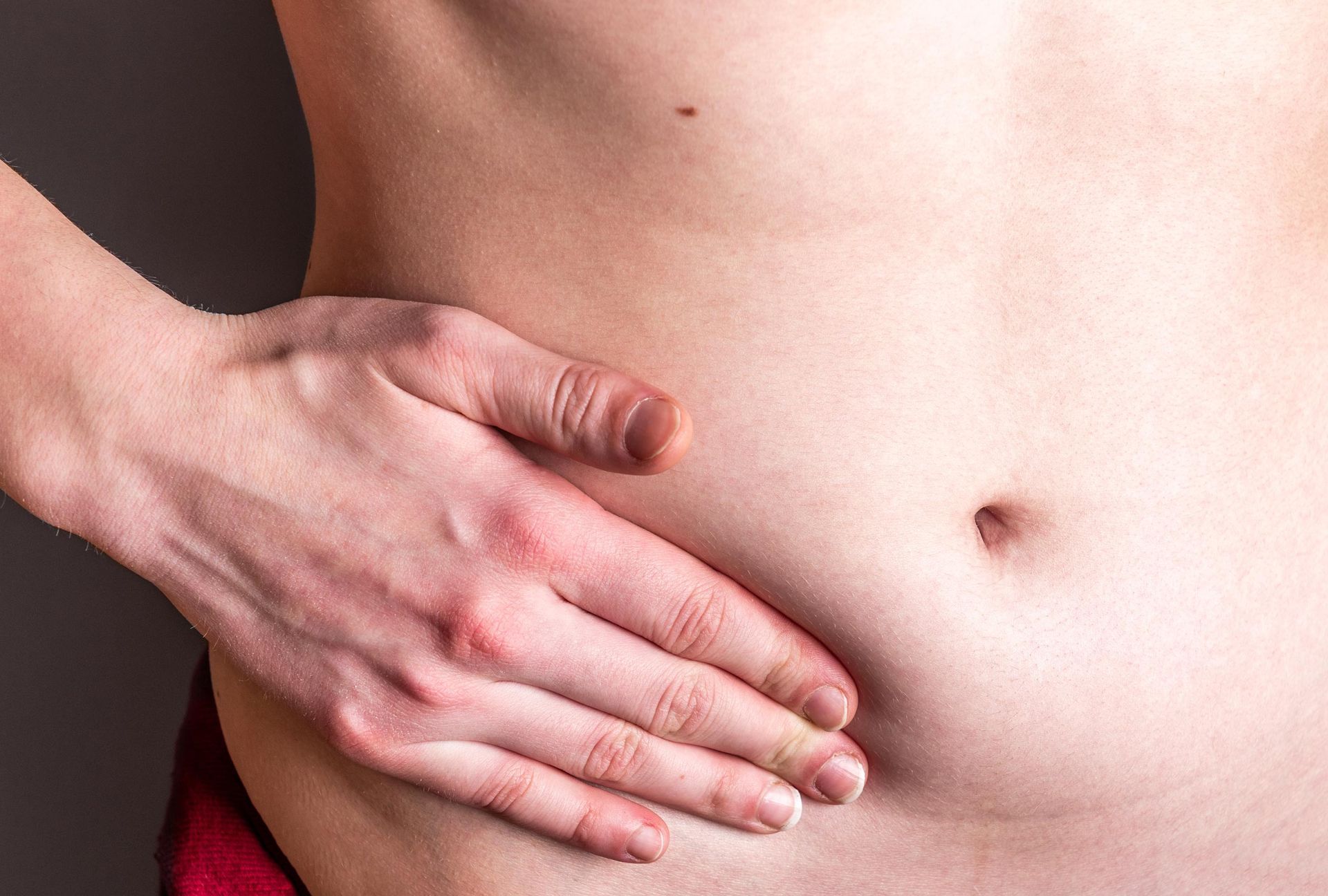
A hernia is a medical condition where an internal part of the body, such as an organ or tissue, pushes through a weak area in the muscle or surrounding tissue, creating a bulge. It can develop in various body parts, most commonly in the abdomen.
A combination of muscle weakness and strain can cause hernias. Factors such as ageing, chronic coughing, heavy lifting, or persistent
constipation may also contribute to developing hernias.
ARE ALL HERNIAS TREATED WITH SURGERY?
Not all hernias require surgical intervention. Sometimes, small hernias may not cause noticeable symptoms and can be treated through lifestyle adjustments and monitoring. However, surgery may be recommended based on the following factors.
Symptoms and discomfort:
- Pain: Persistent or increasing pain around the hernia site may indicate the need for surgery.
- Discomfort: If the hernia causes significant discomfort, impacting daily activities or quality of life, surgery may be recommended.
Size and type of hernia
- Large hernias: Hernias that are large or increasing in size may be more prone to complications and often require surgical intervention.
- Irreducible or incarcerated hernias: Hernias that cannot be pushed back into place or become trapped may lead to complications, necessitating prompt surgery.
Complications
- Strangulation: When a hernia becomes strangulated, meaning blood supply is compromised to the bowel which has been trapped in the sac, emergency surgery is crucial to prevent tissue damage.
- Obstruction: Hernias causing
bowel obstruction may require surgical correction to restore normal bowel function.
WHAT ARE THE COMMON SYMPTOMS OF A HERNIA THAT MIGHT REQUIRE SURGERY?
Common symptoms of hernias that may necessitate surgery include:
- Visible bulge: A noticeable lump or bulge in the affected area, especially when standing or straining.
- Pain or discomfort: Persistent pain or discomfort, particularly during physical activity.
- Gastrointestinal issues: Symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or difficulty with bowel movements may indicate a more severe hernia.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF HERNIA SURGERY?
Open surgery
: Open hernia surgery involves making a single, larger incision directly over the hernia site. This traditional approach provides direct access to the herniated tissue and allows the surgeon to repair and reinforce the weakened area.Laparoscopic surgery
: A minimally invasive surgery using small incisions and a laparoscope camera to guide the surgeon. This procedure is performed with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues.HOW IS HERNIA SURGERY PERFORMED?
During hernia surgery, the surgeon aims to reposition the herniated organ or tissue and strengthen the weakened muscle or tissue. The following is how the procedure is performed, step by step.
Anaesthesia
Hernia surgery is performed under anaesthesia to ensure the patient is comfortable during the procedure. The type of anaesthesia used can vary and is typically discussed with the patient beforehand.
Incision or laparoscopic approach
The surgeon may opt for either an open hernia surgery with a single, larger incision or a laparoscopic approach with several small incisions. Laparoscopic surgery involves using a fibreoptic camera (laparoscope) to guide the surgeon and perform the repair.
Hernia reduction
The herniated structures are reduced back into their normal position, known as hernia reduction.
Repair and reinforcement
The primary goal of the surgery is to strengthen the weakened area to prevent a recurrence, and can be achieved through different techniques.
- Suturing (Herniorrhaphy): The surgeon may use stitches to repair the weakened tissue and close the hernia opening.
- Mesh placement (Hernioplasty): A synthetic mesh is placed over the weakened spot to reinforce the area and provide additional support. It is the standard of care technique, both in open and laparoscopic procedures.
Closure of incisions
If an open surgery is performed, the surgeon will close the incision with sutures or staples. In laparoscopic surgery, the small incisions may require fewer suturing for closure.
Postoperative care
Post-surgery, patients are monitored in a recovery area. Depending on the type of surgery, patients may be able to go home on the same day or require a short hospital stay.
Pain management and specific postoperative instructions are also provided to support a smooth recovery.
WHAT IS THE COST OF HERNIA SURGERY IN SINGAPORE?
The cost of hernia surgery in Singapore depends on the type of surgery, the hospital, and the surgeon's fees. It is best to consult your healthcare provider for a detailed expense estimate.
CAN HERNIAS COME BACK AFTER SURGERY?
While hernia surgery is generally effective, there is a small risk of recurrence. Factors such as the surgical technique, the patient's overall health, and adherence to postoperative care instructions can influence the likelihood of a hernia returning. The internationally recognized risk of recurrence following a well-constructed repair is in the range of 1%.
Regular follow-ups with the
surgeon are crucial to monitor the healing process.
WHAT ARE THE POTENTIAL RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS OF HERNIA SURGERY?
Like any surgical procedure, hernia surgery carries some risks and potential complications. These include infection, bleeding, adverse reactions to anaesthesia, and the development of chronic pain.
It would be best to discuss these risks with your surgeon beforehand to make informed decisions about your healthcare.
ARE THERE ANY HERNIA TREATMENT OPTIONS OTHER THAN SURGERY?
The truth of the matter is this - once a hernia develops, it will not disappear or heal on its own without any form of repair. It will either remain the same in size or more often than not, increase in size and weakness with time. Surgery to repair the defect is the only form of definitive treatment for hernias. All other management options do not address the problem and merely help with symptom relief.
In some instances, lifestyle changes and conservative treatment can help alleviate hernia symptoms without surgery. These may include:
- Dietary modifications: Avoiding heavy meals, spicy foods, and keeping to a healthy weight can help manage symptoms.
- Physical activity: Regular, moderate exercise can strengthen abdominal muscles and reduce the risk of hernias.
- Monitoring: Small hernias without symptoms may be monitored under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
CALL YOUR GENERAL SURGEON FOR HERNIA TREATMENT IMMEDIATELY IF:
- The bulge becomes tender, swollen, or discoloured.
- Severe pain or nausea accompanies the hernia.
- Difficulty passing stool or gas occurs.
Early intervention and proactive management contribute to successful outcomes in hernia treatment.
HERNIA SURGERY IN SINGAPORE
Understanding hernia and its treatment is pivotal for those seeking to overcome it. Whether opting for open surgery or embracing the minimally invasive advantages of laparoscopic procedures, patients choosing hernia surgery can be hopeful for recovery.
Consider seeking assistance from Colorectal Clinic Associates for specialised care in hernia surgery. Our experienced team of surgeons in Singapore can provide personalised treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
Schedule a consultation to learn more about gallstone removal.